|
LIFE SCIENCE |
Chapter 4
Notes Over Text
Many organisms start as just one cell. The number of cells in your body changes as you develop. Your body is constantly changing; even after growth stops.
Red blood cells are produced at a rate of 2 to 3 million per second.
Cells go through ____________ as they live. The time it takes to complete a cell cycle depends on the type of cell. It may be 20 minutes or 19 hours.
Most of a cell’s life is spent in ____________ which is a state of rapid growth, DNA synthesis, and division prep. Cells that no longer divide are always in interphase. The ____________ and muscle cells in one’s body are examples of these.
____________ – is the process in which the nucleus divides to form two identical nuclei with the same number and type of chromosomes as the original. The steps of mitosis are ____________ , ____________ , ____________ , and ____________ .
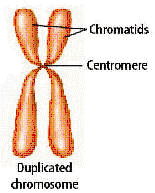 ____________
– are structures in the nucleus that contain DNA. You can only see these
when the cell is dividing.
____________
– are structures in the nucleus that contain DNA. You can only see these
when the cell is dividing.
____________ – are tightly coiled thickened, identical strands of chromosomes.
____________ – is a region that holds together double stranded chromosomes. It is the center of the X.
|
MITOSIS |
|
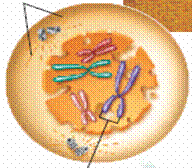
| 1. ____________ – rapid growth, DNA synthesis, and division prep. | |
 |
2. ____________ – chromosomes are now visible, the nuclear membrane is gone, and centrioles move to opposite ends of cell, and spindles begin to stretch across the cell. |
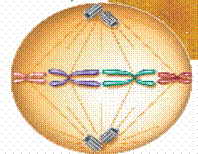 |
3. ____________ – double stranded chromosomes line up across the center of the cell and centromeres become attached to a spindle fiber. |
 |
4. ____________ – centromeres divides, chromosomes separate and begin moving toward opposite ends of the cell. |
 |
5. ____________ – centrioles and spindle fibers disappear. Chromosomes stretch out and are harder to see. Nuclear membrane forms around mass of chromosomes and a new nucleolus appears in each new nucleus. |
After the nucleus divides, the cell’s cytoplasm separates and two cells are formed by pinching in the cell membrane. Interphase begins again with rapid growth in both new cells.
Within a plant cell the cell wall cannot pinch in. Thus a new ____________ is formed which becomes the cell wall between the two new cells.
The result of mitosis is ____________ identical ____________ that are exactly like the mother cell.
____________ is the process by which an organism produces others of its same kind. There are two types – ____________ and ____________ (remember that a or an on the front of a science word means without)
· ____________ reproduction – is the production of new offspring from one parent.
o ____________ – is the division of an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copies its genetic material and then divides into two identical organisms.
o ____________ – occurs when a new organism grows from the body of the parent organism. When the bud can live on its own, it ‘pops’ off.
o ____________ – a whole organism may develop from just a piece of the parent organism. Some organisms replace missing or damaged parts while others can produce an entire organism.
· ____________ Reproduction – is the making of a new organism from the uniting of two sex cells which are called gametes.
o ____________ – sex cell from male.
o ____________ – sex cell from female.
o ____________ – is the uniting of egg and sperm.
o ____________ – The single cell that forms is called a zygote.
Sex cells have only half of the chromosomes so when 2 are united the total is the same as body cells. The production of sex cells is called Meiosis.
Cells that have pairs of similar chromosomes are called ____________ .
Cells that have only half of the chromosomes (1 of each) are called ____________ . Sex cells must be haploid.
____________ is the production of haploid sex cells. Two divisions of the nucleus occur during meiosis – ____________ and ____________ .
Phases of meiosis:
1. ____________ – chromosomes are double and spindle fibers appear. Nucleus membrane is dissolved. Each duplicated chromosome comes near its similar duplicated mate.
2. ____________ – the chromosomes line up in the middle and centromeres become attached to spindle fibers.
3. ____________ – chromosomes separate and are pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
4. ____________ – cytoplasm divides and two cells form.
5. ____________ – chromosomes and spindles reappear.
6. ____________ – chromosomes line up in the middle and attach to spindles. Each centromere now attaches to two spindle fibers instead of one.
7. ____________ – centromere divides, chromatids separate and move to ends of cell.
8. ____________ – spindles disappear, nuclear membrane forms and cytoplasm divides.
The result of meiosis is ____________ cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell (haploid).
____________ are mistakes or changes in DNA of an organism. Mistakes during these divisions do occur. In plants mistakes are common; in animals mistakes are rare. In zygotes produced from sex cells with mistakes death may occur or the zygote may not grow normally.
____________ – deoxyribonucleic acid – is the master copy of an organism’s information. It controls the cells activities with coded information. Every body cell contains the body’s entire set of codes.
In 1952, ____________ discovered that DNA was a double spiral form by using x-rays.
In 1953, ____________ and ____________ made a model of the DNA molecule.
This model is still used today. It shows a ____________ shape (which looks like a ladder that is twisted).
· The sides are made of ____________ (deoxyribose) and ____________ molecules.
· The Stairs are made of ____________ .
o ____________ , ____________ , ____________ , and ____________ are the bases.
o ____________ always pairs with ____________
o ____________ always pairs with ____________
DNA copies itself by unwinding, ‘unzipping’ the molecule using an enzyme, attaching new bases and finally new sugar and phosphate groups.
____________ – are parts of the DNA molecule that directs the making of a specific protein. The entire organism’s traits are controlled by the production of certain proteins. Proteins are made of chains of hundreds or thousands of ____________ in a specific order. Genes are sometimes turned on or off.
Genes are found in the nucleus, but proteins are made on ribosomes. The codes are carried there by the ____________ – ribonucleic acid.
RNA is different from DNA because it is only single stranded, it contains ____________ instead of thymine, and it contains ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose sugar.
There are three types of RNA
1. ____________ RNA (mRNA) carries the information to the ribosome.
2. ____________ RNA (rRNA) makes up the ribosome.
3. ____________ RNA (tRNA) is in the cytoplasm and picks up the appropriate amino acid to attach together to form the protein.
____________ do occur during cell reproduction. This is a permanent change in a gene or chromosome of a cell. These mutations may be caused by factors such as X rays, sunlight, and chemicals.
If the mutation occurs in a body cell, it may or may not be life threatening. Some mutations are harmless or even beneficial. If it occurs in a sex cell, the organism may not survive because all cells of the organism will have the mutation.
Mutations may add variety to a species – which is the basis of evolution.